
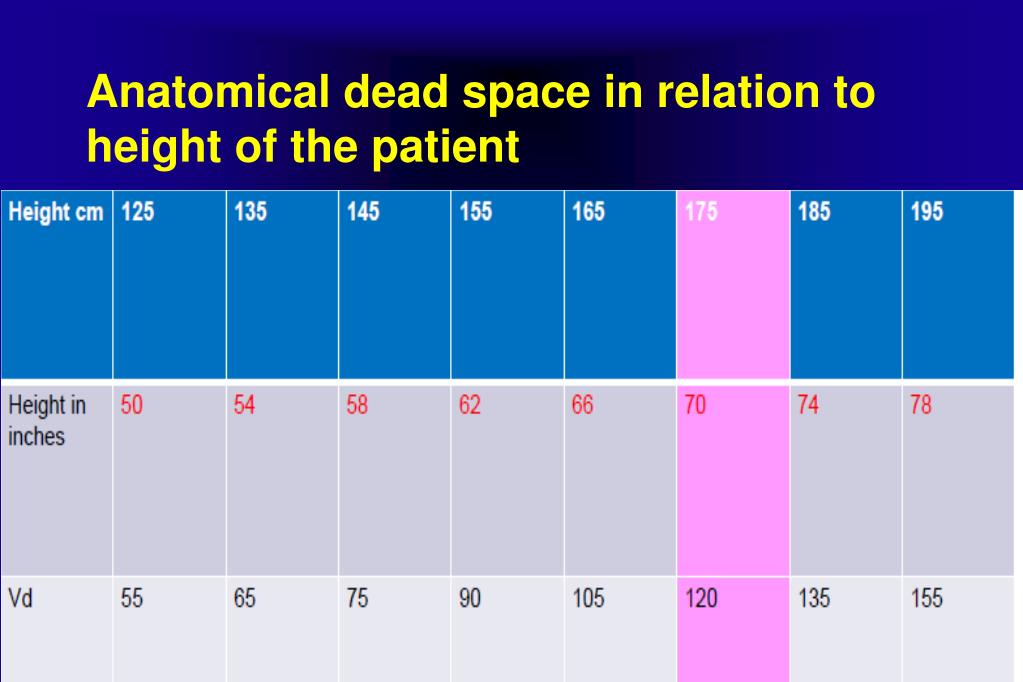
Patient and surgical characteristics, and the respiratory and hemodynamic parameters at T Baseline (20 min after the initial setting). Abbreviations: VD phys, physiological dead space VD aw, airway dead space VD alv, alveolar dead space VD shunt, shunt dead space V TE, expired tidal volume VCO 2, expired tidal volume of CO 2 FCO 2, fractional concentration of CO 2 P ECO 2, mixed expired partial pressure of CO 2 P ETCO 2, end-tidal partial pressure of CO 2 P ACO 2, alveolar partial pressure of CO 2 and PaCO 2, arterial partial pressure of CO 2 are expressed as FCO 2 in this figure.ĬONSORT diagram of patient recruitment for the comparison of volume-controlled ventilation and pressure-controlled inverse ratio ventilation. Thus, alveolar dead space (VD alv) is calculated as VD resp−VD aw, shunt dead space (VD shunt) is calculated as VD phys−VD resp. The volume from the start of expiration to the partial pressure of mixed expired CO 2 point on the Y axis is defined as respiratory dead space (VD resp). The VD aw is determined by applying Fowler’s equal area method (area A equals to B). Phase II ends at the inner square area maximum point. Phase I represents CO 2-free and pure dead space, phase II represents the transition between airway and alveolar gas, and phase III represents alveolar gas. The expired tidal volume on the Y axis is plotted against the partial pressure of expired CO 2 on the X axis in order to express the curve of ‘Volume = VCO 2/FCO 2’. Components of dead space and volumetric capnography.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
